If you’re keeping up with the latest developments in type-2 diabetes and weight loss treatments, you may already know about tirzepatide and Ozempic. These two drugs have been making waves when it comes to managing the symptoms of diabetes and treating chronic obesity.
But what exactly are each of these drugs, and how do they compare to each other?
In this article, we’ll cover:
- What tirzepatide is
- What Ozempic is
- The main differences between the two drugs
- How they affect blood sugar levels
- How they affect body weight management
- The active ingredients in both drugs
- Recommendations around dosage for the management of type-2 diabetes
- Whether tirzepatide or Ozempic is better for weight management
- Whether or not you can take both drugs together
- Frequently asked questions.
There’s plenty to explore, so let’s get straight into it!
What Is Tirzepatide?
Tirazepatide, often sold under the brand name Mounjaro, is developed by pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly. It’s primarily used for people with type-2 diabetes and is part of the GLP-1 receptor agonists class (glucagon-like peptide-1).
In addition to mimicking GLP-1, it is also a glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonist. Together, these two hormones are able to affect signals sent to the brain around food intake. For this reason, it also aids with weight management.
Health Canada has approved tirzepatide for the management of type-2 diabetes alongside lifestyle intervention measures, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, and presents various options for diabetes management. It is not approved as a sole weight management tool.
Eli Lilly is currently working on phase three in the development of tirzepatide for adults who are obese or overweight with weight-related conditions.
History of Eli Lilly’s Involvement with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists1
Tirazepatide is not Eli Lilly’s first experience with developing GLP-1 receptor agonists.
In 2014, they released a dulaglutide drug, known by brand name Trulicity, to manage symptoms of type-2 diabetes. Trulicity is also a GLP-1 receptor agonist. However, tirzepatide is a twincreatin, which can lead to improved glycemic control as well as can result in side effects associated with weight loss.
Eli Lilly’s Role in the Development of Tirzepatide1
Eli Lilly initially applied for a patent for a method of glycemic control that utilized terzapatide in 2016. From there, it was evaluated through clinical trials with a number of participants for effectiveness and safety, passing three. In 2022, they announced that the drug had also successfully met their criteria for treatment for obese and overweight patients.
It is subject to continued research and development for improved efficacy and, as of June 2023, is in phase three for treatment of obesity.
According to GlobalData, drugs that progress to phase three for obesity have a 44% success rate for phase transition. It is speculated that this drug will be approved for weight loss by the end of 2023.
What Is Ozempic?
Ozempic is one of many brand names for the drug semaglutide, a medication developed in 2012 by Novo Nordisk.
You may have heard this medication be referred to as Wegovy or Rybelsus. It is prescribed for type-2 diabetes management, as well as weight management in adults with a BMI of 27 or over.
Similar to tirzepatide, this medication is also part of the GLP-1 receptor agonist class family, and mimics the GLP-1 hormone. This results in insulin production which encourages glucose reduction. It has a side effect of appetite suppression, which helps reduce body weight in adults with diabetes.
Ozempic is often prescribed after other diabetes medications have already been trialed for a period of time, eg, metformin.
Tirzepatide vs Ozempic - What’s the Difference?
The main difference between tirzepatide and Ozempic is their mechanism of action. Tirzepatide is a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, while Ozempic (semaglutide) targets only the GLP-1 receptor. Tirzepatide may provide greater weight loss and blood sugar control, but both are effective for type 2 diabetes management.
Some other differences between these two medications is the distribution, clinical studies, and research surrounding them.
Ozempic has been on the market far longer than tierzapatide, is more accessible and has more research backing it. Additionally, it is approved for weight management in those with a BMI over 27, while tirzepatide is currently only available for treatment of type 2-diabetes.
Another notable difference is that Ozempic has been approved as a medication that can potentially impact cardiovascular health in those suffering from type-2 diabetes; tirzepatide has not yet been approved for this.
Tirzepatide vs. Ozempic Side Effects
Tirzepatide vs. Ozempic. Blood Sugar Levels
Tirzepatide and Ozmepic work slightly differently due to the fact that tirzepatide activates both GLP-1 receptors and GIP pathways, making it a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. Ozempic, on the other hand, does not activate GIP pathways.
Knowing how and why these two drugs fall into two distinct medication classes will help us understand how they affect blood sugar levels differently.
How Tirzepatide and Ozempic Affect Blood Sugar Levels
GLP-1 receptors are targeted by both tirzepatide and Ozempic. They are proteins located on the beta cells of the pancreas and brain neurons. Since the pancreas is the organ responsible for insulin production, GLP-1 receptors promote insulin secretion in the presence of high blood sugar levels.
Medications like tirzepatide and Ozempic stimulate these receptors in order to get them to do what they do best: produce more insulin when blood sugar levels are high. This, in turn, combats these high blood sugar levels and aids in lowering blood glucose.
GIP pathways are activated by tirzepatide. GIP is a hormone that lives in your small intestine. When you eat food, the GIP hormone produces insulin to combat the rise in glucose, which in turn aids in lowering your blood sugar levels.
So, the main difference between how tirzepatide and Ozempic affect blood sugar levels comes down to what they target in your body. Tirzepatide targets both GLP-1 and GIP, utilizing both your pancreas and small intestine to lower blood sugar, whereas Ozempic only targets GLP-1.
Results from Clinical Trials on Blood Sugar Control with Tirzepatide and Ozempic
Several clinical trials have been conducted and articles written in order to evaluate both tirzepatide and Ozempic’s effectiveness in controlling blood sugar levels. These studies have shown differing results in clinical trials.
In a 2021 study, a 40-week trial was conducted in which 1879 patients received a dose of either tirzepatide or semaglutide (Ozempic) once weekly.
Changes in blood sugar level were monitored throughout this trial. By the end of the 40 weeks, blood sugar was observed to be reduced by tirzepatide -2.01 percentage points (5mg), -2.24 percentage points (10mg), and -2.30 percentage points (15mg). Ozempic was observed to reduce blood sugar levels by -1.86 percentage points (1mg).
The study showed how Tirzepatide and Ozempic influences HbA1c levels differently. While both were successful in reducing and controlling blood sugar, tirzepatide had “greater reductions than those with semaglutide in the patient-measured mean blood glucose levels at all seven time points.”
Tirzepatide vs. Ozempic. Body Weight Management
While both tirzepatide and Ozempic are known to aid in body weight management in patients with type 2-diabetes, due to the different ways that these two medications function, there is some variation in effectiveness.
It is important to note that the way that these drugs contribute to weight loss is entirely dependent on the patient’s individual needs and how their body responds.
Effectiveness of Tirzepatide and Ozempic for Weight Loss in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Body weight management in patients with type-2 diabetes is something that tirzepatide and Ozempic can both aid in. But how effective are they when it comes to weight loss in adults with type-2 diabetes?
In a 2022 study, changes in body weight resulting from both tirzepatide and Ozemic were analyzed and compared. The data showed that the use of tirzepatide resulted in an overall average weight loss of 17.8%, while Ozempic use resulted in a weight loss of 12.4%.
This displays differing levels of efficacy in weight loss, with tirzepatide slightly more effective.
Results can vary depending on the individual, meaning these results may not accurately reflect which medication would work best for you, especially as they both require careful administration by patients.
Patients should consult their medical team when considering a drug, so that the right drug may be chosen based on the patient’s health condition. All new drugs require careful monitoring by healthcare professionals, especially when related to weight management.
Common Side Effects Associated With Weight Loss When Using GLP-1 Medications
When taking any GLP-1 medications to aid with weight loss, there will be a range of side effects to look out for, and both tirzepatide and Ozempic show varying degrees of side effects.
Some common side effects associated with GLP-1 medications are:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Stomach pain
- Constipation
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Indigestion
- GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease)
- Bloating.
If you experience any of these side effects and find that they are lasting an extended period of time or are worsening to a considerable degree, contact your medical team immediately.
Active Ingredient Differences Between Tirzepatide and Ozempic
Though tirzepatide and Ozempic have similar functions, there are several differences between the two. One is the fact that they have a different active ingredient composition.
Tirzepatide is an active ingredient in itself: it is the active ingredient in the brand Mounjaro.
Ozempic, on the other hand, is the brand name for the drug with the active ingredient semaglutide. The other names of semaglutide brands are Wegovy and Rybelsus, which function generally the same, but are marketed in different regions and for different purposes.
There is also a significant difference between the active ingredients tirzepatide and semaglutide (Ozempic).
Since tirzepatide targets both the GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonists, this active ingredient functions much differently than semaglutide, which only targets the GLP-1 receptor agonist.
Both drugs might require dietary adjustments while using, and should be taken along with lifestyle intervention measures, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, for best results.
Dosage Recommendations for Use in Type-2 Diabetes Management
When using any type of medication, it is extremely important to follow the dosage instructions given to you by your medical team.
Taking too little of the medication may render it ineffective, and taking too much can be extremely dangerous and lead to severe side effects and negative impacts on your health.
If you have any questions or concerns regarding your medication dosage, be sure to approach your medical team for further information, or to discuss things of concern.
Maximum Doses Recommended by Healthcare Providers for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
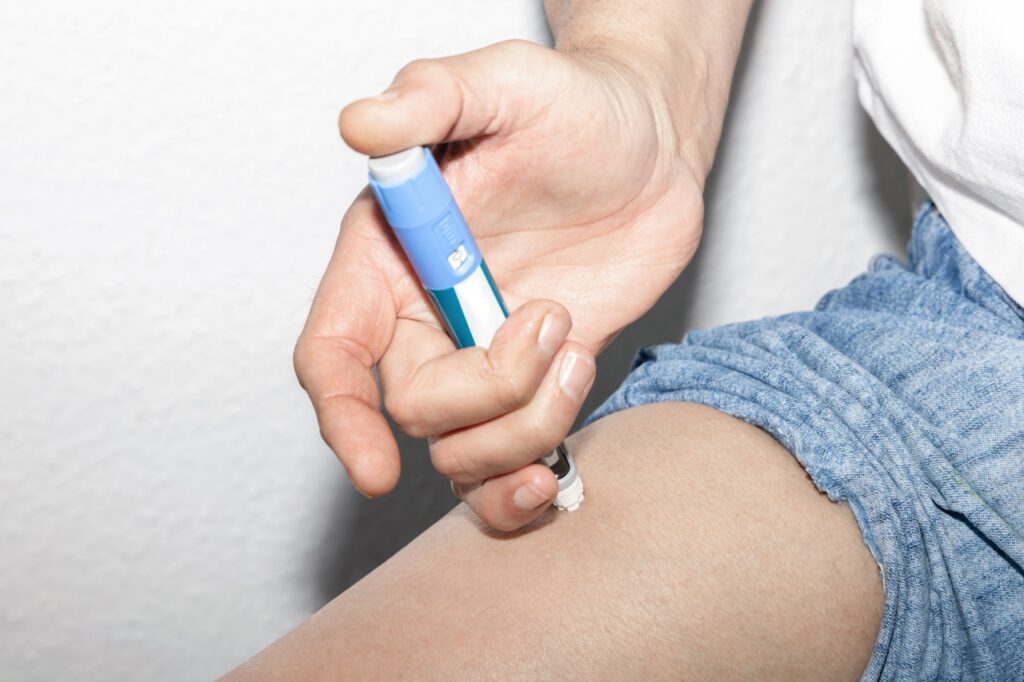
When prescribed Ozempic, you will likely start on a lower dose, and then increase it to a higher maintenance dose at the four-week mark. The drug is available as an oral pill, or can be injected for blood sugar control.
Dosages differ depending on which form you take and require specific dosage recommendations for type-2 diabetes patients.
Ozempic oral dosage:
- Initial dose: 3 mg once daily for 30 days, followed by 7 mg daily
- Maximum dose: 14 mg once daily. Taking two 7 mg tablets rather than on 14 mg tablet is NOT recommended.
Ozempic subcutaneous dosage:
- Initial dose: 0.25 mg once weekly for 4 weeks, followed by 0.5 mg once weekly
- Maximum dose: 2 mg weekly.
If you require further blood sugar control, the dose may be increased to either 1 mg or 2 mg.
A tirzepatide prescription generally also requires a gradual increase in dosage until the required amount is reached. Tirzepatide is currently not available in oral form and will need to be administered subcutaneously via weekly injections.
Tirzepatide subcutaneous dosage:
- Initial dose: 2.5 mg once weekly for 4 weeks, followed by 5 mg once weekly
- Maximum dose: 15 mg weekly.
If you require further blood sugar control, the dose may be increased.
Titration Recommendations for Both Drugs for Optimal Blood Sugar Control
If after taking the standard doses of tirzepatide and Ozempic to little or no effect, you may require dosage titration for optimal blood sugar control.
Ozempic:
- Oral titration: If the standard dose of 7 mg daily is ineffective for 30 days, you may be prescribed the 14 mg (maximum dosage) tablet
- Subcutaneous titration: If the standard dose of 0.5 mg weekly is ineffective for 4 weeks, you may be increased to the 1 mg injection. If this dosage is ineffective for a further 4 weeks, you may be increased to the 2 mg (maximum dosage) injection.
Tirzepatide:
- Subcutaneous titration: If the standard dose of 5 mg weekly is ineffective for 4 weeks, you may be increased by 2.5 mg every 4 weeks until efficient dosage is achieved or maximum dosage (15 mg weekly) is reached.
This method of gradually increasing the dosage not only helps to gauge what level is the most effective to you and the way your body responds to the medication, but also lessens the gastrointestinal side effects of these drugs which presents long-term implications for users.
Which is Better for Weight Loss — Tirzepatide or Ozempic?
Many clinical trials studies on the weight loss effects of tirzepatide and Ozempic respectively have been published over the last few years. However, when comparing the results of these studies, tirzepatide (the newer drug on the market) appears to be more effective than Ozempic when it comes to weight loss and could potentially replace other GLP-1 medications.
A 2022 study comparing the weight loss effects of tirzepatide versus Ozempic in patients with type-2 diabetes found that tirzepatide resulted in a weight loss of 17.8% compared with 12.4% for Ozempic. This makes tirzepatide better value, based on effectiveness and cost.
Furthermore, a 2023 study on the effectiveness of tirzepatide for weight management found that it “provided substantial and clinically meaningful reduction in body weight,” with the results comparable to a 2021 study on the effectiveness of Ozempic for weight management.
The Ozempic trial tested patients who did not have diabetes, and was solely focused on weight management, whereas the tirzepatide trial was focused on the weight management of patients who also had type-2 diabetes.
Patients with both diabetes and obesity often have a much harder time losing weight. The fact that these two trials are on par with each other suggests that tirzepatide is more effective than Ozempic.
However, it is important to reiterate that tirzepatide has not yet been approved for the sole purpose of weight loss, though this appears to be on the horizon.
Both of these medications have their own pros and cons when it comes to their effectiveness in managing body weight.
Can You Take Tirzepatide and Ozempic Together?
It is not recommended that you take tirzepatide and Ozempic together. Combining these two medications could increase the probability or intensity of side effects, and can put you at a higher risk of severe health complications.
Though taking more than one GLP-1 drug at a time is generally not recommended, there is a chance that both may be considered for combined use in treatment with other diabetes medication. Be sure, though, to never take any two medications together without approval from your medical team, even if you believe they won’t interact negatively with each other.
Key Takeaways
While both tirzepatide and Ozempic are similar and used to treat the same symptoms, there are unique pros and cons that come along with them.
Each drug has slightly different effects on blood sugar, weight management, and side effects, and may react differently depending on your personal circumstances and medical history.
It’s also important to note that there may be certain contraindications with both drugs, so be sure to discuss with your medical team if you’re considering either.
FAQs
What are the Long-term Implications of Using Tirzepatide vs. Ozempic?
Extended use of tirzepatide or Ozempic may present long-term implications for users. There are of course common side effects (primarily gastrointestinal), but these should not continue for any extended period of time, and are most common when beginning the drug or changing your dose.
There are some long-term side effects that come along with these drugs, though they are uncommon, that you should look out for. These include:
- Digestive problems
- Gallbladder problems
- Allergic reaction
- Pancreatitis
- Increased risk of thyroid cancer
- Kidney issues
- Hypoglycemia.
If you experience any of these more serious side effects, discontinue your use of the drug immediately and contact your medical team, or the ER at your local hospital.
In addition, there are a separate set of risks that come along with stopping either of these medications, such as increased appetite, regaining weight, and of course spikes in blood sugar.
Due to the fact that both of these medications (particularly tirzepatide) are relatively new, many long-term effects are not yet known. Both are subject to continued research and development.
Are There Any Dietary Restrictions When Using Tirzepatide or Ozempic?
There are no strict dietary restrictions that you need to follow while taking either tirzepatide or Ozempic, but there are foods that you should avoid to lessen the gastrointestinal side effects.
Foods high in fat and sugar are harder for your body to digest, will contribute to any nausea that you may feel while taking these medications, and directly contradict the effects of the drug.
If you are taking these medications for weight management, it is recommended that you pair them with a healthy, low-calorie diet and regular exercise.
How Does Each Drug Impact Cardiovascular Health?
Ozempic has been approved to reduce cardiovascular disease risk in patients who have type-2 diabetes and heart disease, whereas tirzepatide has not. However, a 2022 trial showed that tirzepatide did not increase the risk of major cardiovascular events in patients with type-2 diabetes.
Other studies suggest possible cardiovascular benefits may come along with tirzepatide usage, though more extensive research and clinical trials will need to be performed before approval.
Ozempic, on the other hand, has significant evidence to suggest that it is successful in reducing cardiovascular disease risk in patients with type-2 diabetes.
A two-year-long trial in 2016 indicated that semaglutide (Ozempic) “significantly reduced the risk of the occurrence of a 3-component MACE endpoint consisting of cardiovascular death, non-fatal heart attack, or non-fatal stroke.” This trial contributed to Ozempic’s approval.











 (US)
(US)