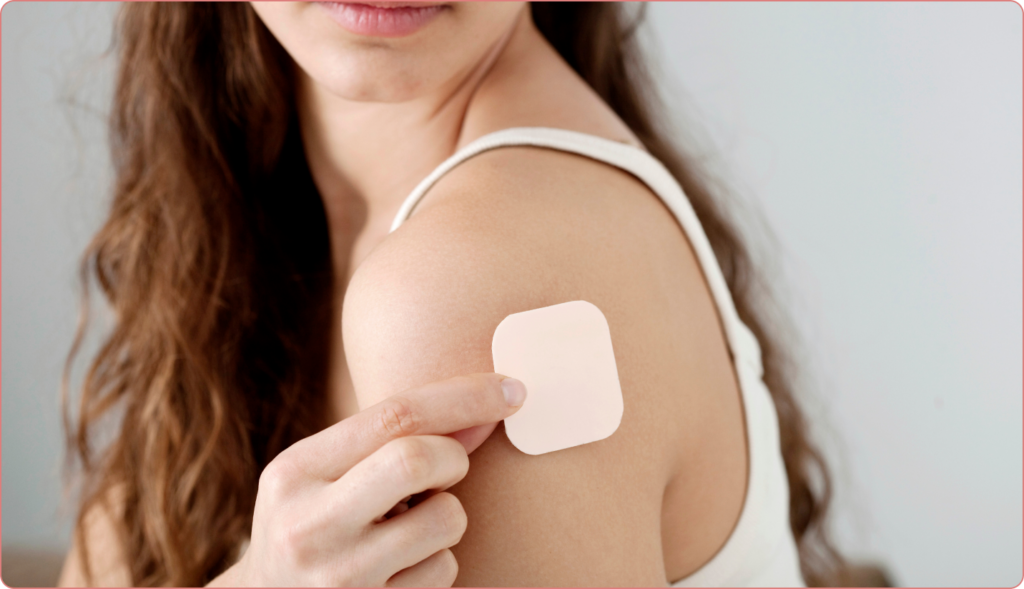
There are many different types of birth control available today. One such method is the birth control patch. In Canada, this patch continually releases ethinyl estrogen and norelgestromin (a type of progestin) into your skin for 24 hours. These hormones work to prevent ovulation, so there is no egg available to fertilize. It also makes it harder for sperm to reach the egg, by thickening the cervical mucus.
What is it used for?
The main reason why individuals use the birth control patch is to prevent pregnancy. However, others may use the patch to regulate irregular cycles, decrease excessive menstrual blood loss, painful periods, acne, endometriosis, and more.
Other individuals can find it hard to take a treatment method daily, like the birth control pill emands, so the patch is a welcome alternative as it only has to be changed once a week. It can also be a suitable alternative for those who have issues swallowing pills.
How effective is it?
As long as individuals wear the patch correctly and change it as directed, it’s been shown to be very effective in preventing pregnancy. However, if individuals are late changing the patches or leave it off for long durations, they significantly increase the risk of unintended pregnancy. There is no significant difference in the effectiveness of the birth control patch versus the traditional oral birth control pill if used correctly.
What are the risks?
Many of the risks associated with the birth control patch are similar to the risks associated with other hormonal birth control options, such as:
- headaches
- nausea
- breast tenderness
- menstrual cramps
- vaginal bleeding or spotting
- rarely, it can be associated with blood clots or certain types of cancers
Some side effects specific to the transdermal patch form of birth control include application site reactions and irritation.
How do you use it?
When starting the birth control patch, your doctor will discuss an appropriate start date – your choice of start date will impact if and how long you may need to use backup contraception for, if you are using it to prevent pregnancy.
The patch should only be applied to certain parts of your body: either your buttocks, lower abdomen, or upper outer arms. It should not be applied to your breasts. The application site should be clean, intact, and dry. To avoid skin irritation, the specific application site should be rotated each time.
The patch is quite discreet and can be worn while showering and exercising. On the same day each week the old patch should be removed, and a new patch applied. This is done for three weeks: the last week is a patch-free week. If you are late in applying a new patch, it is important to speak with your pharmacist or doctor so they can advise you on whether you need backup contraception.
How can I get it?
Do you want to try the patch? Great! First, speak with a doctor to make sure it’ll work for you. It is important to let your doctor and pharmacist know if you are taking any other medications – some medications can interact with your birth control patch and render it ineffective. If the patch is an effective and safe option for you, your doctor will provide you with a prescription.
Jill Health has a team of licensed medical professionals who are experts in birth control – talk to one today from the comfort of your home to see if the birth control patch is right for you. Additionally, once your treatment plan is finalized, our team will ship your personalized treatment plan straight to your home!











 (US)
(US)